How to use predictive maintenance to increase efficiency?
Predictive Maintenance is one of the largest application areas of Industrial IoT. But, how to use IoT Predictive Maintenance to increase production efficiency in different industries? What are the benefits, which sensors are available, and how to get started? This blog gives a full overview and examples for IoT Predictive Maintenance!
What is Predictive Maintenance?
Maintenance has always been an intrinsic part of any production. A good maintenance plan ensures safe operations, equipment availability and reduces costs. Maintenance includes the troubleshooting, repairing, controlling and verifying physical equipment, and contributes to the improvement of industrial processes. According to Gouriveau et. al., the last 20 years have meant new requirements for maintenance in terms of quality, safety and costs. As industrial equipment become more complex, they require greater competence in maintenance as well.
IoT Predictive Maintenance Techniques
Predictive Maintenance (PdM) techniques are used to determine when in-service equipment need repairment. Predictive Maintenance, also known as condition-based maintenance, is based on real-time analysis of data from the industrial equipment. The objective is to prevent unexpected failures without costly and inconvenient routine checks, or any unnecessary downtime.
Condition Monitoring
Predictive maintenance requires condition monitoring. This means the continuous monitoring of machines during process, to ensure optimal use. Condition monitoring can be done continuously, periodically and remotely. First, production or machines are monitored continuously, with data collected on critical moments. Periodic monitoring gives analysis over the changing vibration behaviour. And finally, remote monitoring enables the equipment to be kept an eye on from a remote location.
Data Collection and Processing
Data collection and processing is one of the main components of Predictive Maintenance. The data collected can be based on physical phenomena such as vibration, temperature, pressure, voltage, light dispersion or humidity. Other kind of data can be, e.g. process deviations, raw material quality, control settings, or machine specification. Technology has made it possible to monitor machines and equipment continuously. This is done by using different kinds of sensors to assess the degradation and predict the failures ahead of time.
IoT Sensors for Predictive Maintenance
Wireless internet of things (IoT) sensors make the Predictive Maintenance easier than ever before. Further, retrofit IoT sensors allow easier and faster setup, and enable industrial enterprises digitalize old process equipment without large investments.
Here are examples of industrial sensor, which can be used for various IoT Preventive Maintenance use-cases.
- A retrofit angle sensor for measuring the position of manual, rotating hand-operated valves. It is attached to the body of a manual valve. It has magnetic and mechanical angle sensors to monitor the valve’s position, and to report any dispositioned valves to the central operational dashboard of the plant to allow for a rapid fix by the maintenance staff.
- Multi-functional environment sensor which monitors, and wirelessly reports all conditions in the factory – including the temperature, humidity, luminosity, the machine run-time data and more. The sensor is equipped with a rugged IP67 casing, and its replaceable battery can operate up to five years depending on the set transmit interval.

What are the Predictive maintenance Benefits?
The benefits of predictive maintenance are vast, and differ from a case to another, but here are some of them listed:
- Predictive Maintenance can reduce the number of breakdowns
- Predictive Maintenance increases the reliability of production processes
- Personnel safety can be improved through Predictive Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance reduces the periods of inactivity for the equipment
- The company’s performance can be increased by Predictive Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance can increase equipment’s lifetime
In addition to this, predictive maintenance functions can often be made when the equipment is on service. Thus minimizing any interruptions to operations.
IoT Predictive Maintenance Examples
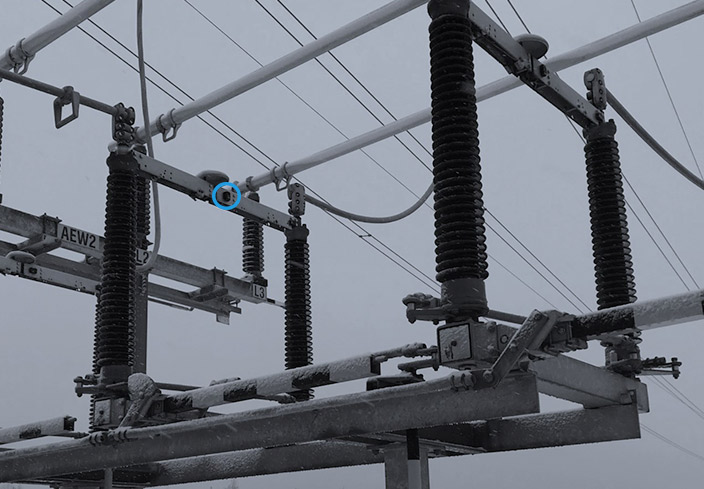
Haltian’s Thingsee IoT platform has been used for several Predictive Maintenance projects. In one of Haltian’s predictive maintenance examples, Finland’s transmission system operator Fingrid shows how IoT solutions can optimize maintenance costs by measuring the temperatures of connecting components in electrical substations
Preventive vs. Predictive Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance (PM) means maintenance that is carried out before the failure occurres. Now, this might sound very similar to predictive maintenance, but Preventive Maintenance techniques include a schedule for periodic checks. These checks are performed to all monitored elements, whether they actually need maintenance or not. According to Gouriveau et al., this “predetermined maintenance can lead to over-care, that is, an excess of useless interventions, and thus financial wastes for the company.” Predictive maintenance is more dynamic, as it takes into account the current condition and attempts to predict the equipment’s state evolution in time.
Another problem with preventive maintenance is the possibility of breakdowns between routine checks. In these cases, unplanned maintenance (or run-to-failure maintenance) is performed when something is already broken which, of course, leads to unknown costs depending on the broken element.
How to get started with IoT predictive maintenance?
In conclusion, a well-planned and implemented Predictive Maintenance is the foundation of any maintenance program. Investing in IoT predictive maintenance for critical operational functions could save you a lot of money in maintenance costs alone, not to mention increased safety. Though predictive maintenance won’t erase all routine checks, it can certainly reduce them.
Luckily, the Internet of Things, new technologies, and digitalization have made the optimization of maintenance possible. The question now is how to get started with IoT Predictive Maintenance. Read how Fingrid did it with us:
Here you can Read More about Predictive Maintenance
- R. Gouriveau, K. Medjaher and N. Zerhouni, From Prognostics and Health Systems Management to Predictive Maintenance 1: Monitoring and Prognostics, 2016
- “Condition Monitoring of rotating machines,” [Online]. Available: https://www.istec.com/en/condition-monitoring-rotating-machines/
- N. Amruthnath and T. Gupta, “Fault Class Prediction in Unsupervised Learning using Model-Based Clustering Approach,” 2018.


